English
繁體中文
简体中文

Feeling down? Wondering if it is more than just a bad day? Imagine if technology could read your emotions and lend a helping hand. With shortage of psychiatrists challenging the global healthcare systems, it can be hard for depression sufferers to get diagnosed. CUHK researchers have harnessed the power of AI technology to develop two innovative tools that make diagnoses easier and earlier: by utilising a pioneering mobile app and looking into your eyes.

Feeling down? Wondering if it is more than just a bad day? Imagine if technology could read your emotions and lend a helping hand. With shortage of psychiatrists challenging the global healthcare systems, it can be hard for depression sufferers to get diagnosed. CUHK researchers have harnessed the power of AI technology to develop two innovative tools that make diagnoses easier and earlier: by utilising a pioneering mobile app and looking into your eyes.

The COVID-19 virus is mutating rapidly. As subvariants like BA.4 and BA.5 emerge, we must act fast to curb the pandemic. Vaccination is the most effective way to control epidemic, but the protection it offers declines as the virus evolves. Predicting vaccine effectiveness in a short time frame is key to winning this battle. CUHK researchers have developed a bioinformatics platform that can provide a snapshot of vaccine effectiveness in real time, instead of it taking months.
Innovative algorithms developed by a CUHK team, using bioinformatics analysis of virus genome, can estimate vaccine effectiveness (VE) by quantifying the relationship between the genetic mismatch between flu vaccines and current virus strains. This real-time prediction method of VE early in flu season gives the government a heads-up in selecting effective vaccines and organising resources before mass vaccination.
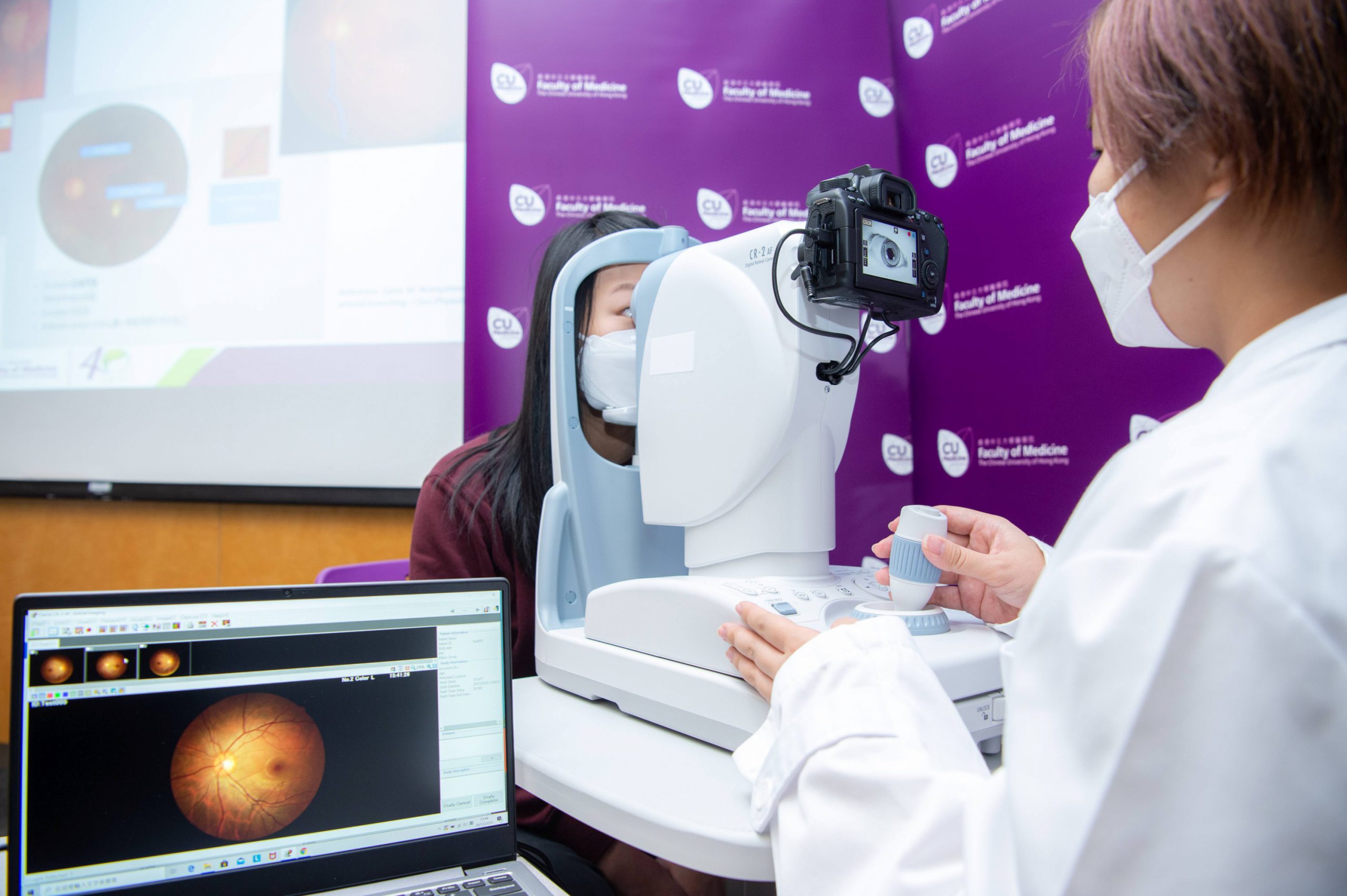
Eyes are the window to the soul, and so to our health. A research team from CUHK has developed Automatic Retinal Image Analysis technology to evaluate the risk of stroke and dementia. Recently, they have extended its application to assess the risk of autism in children by analysing their captured retinal images, hoping to reduce delayed diagnosis or even misdiagnosis.