English
繁體中文
简体中文
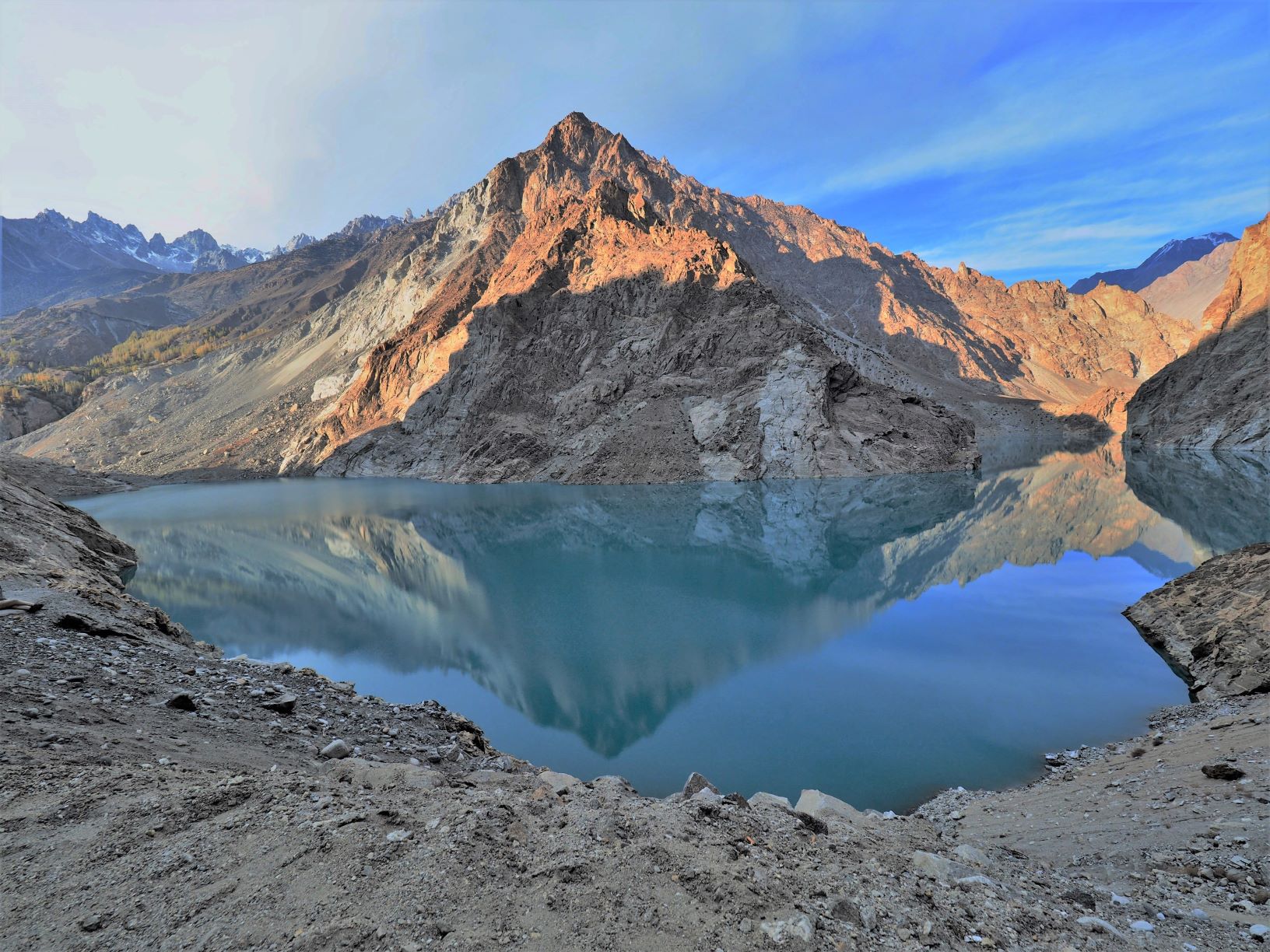

Over 100 earthquakes of magnitude six or higher occur globally each year, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), causing numerous casualties. While plate tectonics are their primary cause, along with other factors such as volcanic activity, understanding and predicting their occurrence remains elusive. Now, a CUHK study has unearthed a novel cause: the stress exerted on faults by landslide-dammed lakes. It offers valuable insights for earthquake risk management and prediction.
Current technology like satellite remote sensing is sharper and faster than the human eye in studying earth terrain for climate change effects but limited in detecting changes to landscape from massive and vast permafrost thawing. A CUHK geophysicist has developed an AI tool “DeepThaw”, a unique algorithm fed by massive numbers of satellite images to detect destabilised slopes over a wide area automatically to address the risk our cryosphere is facing.
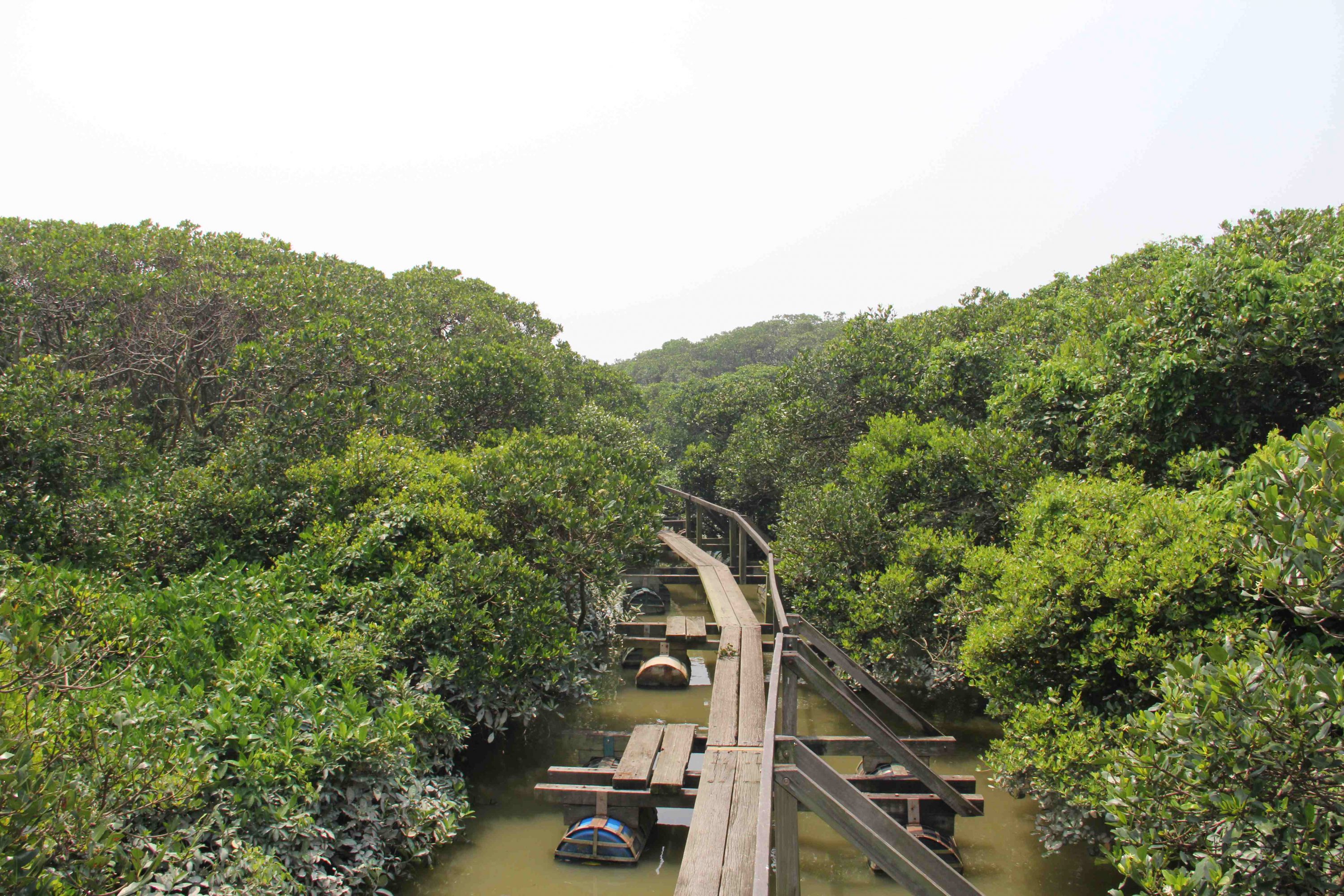

Mangrove wetlands help with climate change by retaining carbon but the methane they emit counters the benefit. An international study shows the good being done by retention is reduced by emission to half over 20 years. And the balance is tipping the wrong way because of global warming and river discharge.